pleural effusion cat ultrasound
TFAST Accurate Diagnosis of Pleural and Pericardial Effusion Caudal Vena Cava in Dogs and Cats. Determining the underlying aetiology is.
Fast Tfast Ultrasound Examinations For Rapid Diagnosis In Emergency Patients Clinician S Brief
This review outlines a practical approach to cases of pleural effusion focusing on early recognition and confirmation of pleural space disease stabilisation of the patient and logical diagnostic investigation.
. TFAST a standardized and validated thoracic point-of-care ultrasound examination includes 5 acoustic windows. Bilaterally applied chest tube site and pericardial site views plus diaphragmatico-hepatic view also part of AFAST Vet BLUE. Diagnostics will be necessary to confirm the cat has pleural effusion and determine a cause.
Classification of pleural effusion PE is central to diagnosis. The aim of this study was to evaluate in 20 cats presented with PE paired samples of serum and pleural. JAVMA 188 8 876-878.
Focused Assessment Sonography for Trauma FAST procedure. Cats presenting with pleural effusion are nearly always in respiratory distress ranging from an increased respiratory rate and effort to open mouth breathing. A chest ultrasound to look for the presence of fluid within the pleural cavity.
X-ray and ultrasound imaging of the chest cavity are also very helpful in analyzing the causative factors. Abdominal ultrasounds were performed in 70 cats with pleural effusion and revealed concurrent abdominal effusion in 59 of these cats. Determining the underlying aetiology is key to appropriate management.
Feline infectious peritonitis. Of the cats that received thoracic ultrasound most exhibited bilateral pleural effusion. Sitting or lying in strange positions to ease breathing.
Vet Radiol Ultrasound 39 3 193-196. Pleural Space Infection Can Become Permanent. Pleural effusion can be confirmed with radiography a single DV view if patient permits or thoracic ultrasonography.
Thirty-two cats that received thoracic ultrasonography were found to have thoracic masses. For this reason an abnormal accumulation of fluid in this cavity causes cats to have respiratory distress which causes them to become agitated. Traditional veterinary classification has distinguished between transudates modified transudates and exudates.
Of these two-thirds 127183. Congestive heart failure CHF. This review outlines a practical approach to cases of pleural effusion focusing on early recognition and confirmation of pleural space disease stabilisation of the.
Tumors in the lungs or chest wall can lead to pleural effusion. Rishniw M et al 1998 Hydrothorax secondary to a perinephric pseudocyst in a cat. The most common causes of pleural effusion in cats are congestive heart failure CHF feline infectious peritonitis FIP cancer chylothorax and bacterial infection.
Pleural effusion was confirmed in all of the cats who had thoracic ultrasonography 128380. This syndrome is caused by infection with a mutated form of a feline coronavirus. The therapeutic intervention also provides your first diagnostic test.
Approximately half of the cats 183380. AFAST and TFAST abdominal and thoracic focused assessment with sonography for trauma triage and tracking constitute limited ultrasound examinations that focus on identifying the presence of fluid within the peritoneal pleural and pericardial spaces. Five cats without radiographic pleural effusion were later confirmed to have pleural effusion via thoracic ultrasound.
This can be caused by thoracic lymphangiectasia swollen lymph vessels that leak chyle into the pleural space congestive heart failure obstruction of the cranial vena cava the major vein that returns blood to the heart from the front of the body cancer fungal infection feline heartworm. Pleural effusion is an accumulation of fluid of a different nature in the pleural space of cats. Major Differential Diagnoses for Pleural Effusion in the Cat.
This non-invasive and quick test can help the veterinarian evaluate the cat quickly. Abdominal abnormalities identified on ultrasound included abdominal masses lymphadenopathy hepatic venous congestion hepatomegaly splenomegaly renal enlargement small intestinal wall thickening steatitis and pancreatitis. In one study these causes accounted for more than 88 of cases with pleural effusion.
When a cat is suffering from pleural effusion the liquid present in the chest cavity prevents the lungs from fully inflating. What are the most common causes of pleural effusion in cats. Vet Radiol Ultrasound 1998.
The most commonly diagnosed cause of pleural effusion in cats is chylothorax. Baker R Lumsden J H 2000 Pleural and Peritoneal Fluids. The rest of the series discusses ultrasound evaluation of specific abdominal organssystems.
Signs of Pleural Effusion in Cats. Fossum T W. 482 had echocardiographic studies.
1986 Immunoglobulin A myeloma in a cat with pleural effusion and serum hyperviscosity. Diverse disease processes result in sufficient fluid accumulation within the pleural space to cause respiratory compromise. A cat with this condition might show some or all of the following signs.
In the latter situations therapeutic intervention must be initiated quickly to prevent respiratory arrest. Diverse disease processes result in sufficient fluid accumulation within the pleural space to cause respiratory compromise. Pleural effusion or pericardial effusion can cause muffled heart sounds.
Rishniw M Weidman J Hornof WJ Hydrothorax secondary to a perinephric pseudocyst in a cat. 694 had obvious pleural effusion and 21183 115 had pericardial. A sample of pleural fluid obtained by piercing the cats chest cavity with a needle will be sent to the laboratory for analysis.
Other sources of information. The pleural space is the gap between the two feline pleurae which line the lung and aid in breathing. In human medicine PEs are divided into only two categories.
In some cats infection with mutated coronavirus can lead to blood vessel damage which results in fluid leakage. 337 including the 5 who had no radiographic evidence of pleural effusion. When FIP affects the chest cavity pleural effusion results.
The type of pleural fluid withdrawn will enable your veterinarian to diagnose the cause of the pleural effusion.
Lung Ultrasound Flooding In Fulminant Pulmonary Oedema In Cats And A Comparison With Pneumonia Vet Practice Support

How To Ultrasound Detection Of Pleural Fluid Case Study Video Youtube

Lung Ultrasound Fundamentals Wet Versus Dry Lung Signs Of Consolidation In Dogs And Cats Veterinary Clinics Small Animal Practice

Pin By Dr Abuaiad On Lymphatics Lymph Nodes Sonography Gut Health

Front Line Ultrasound Imaging Of The Feline Urinary
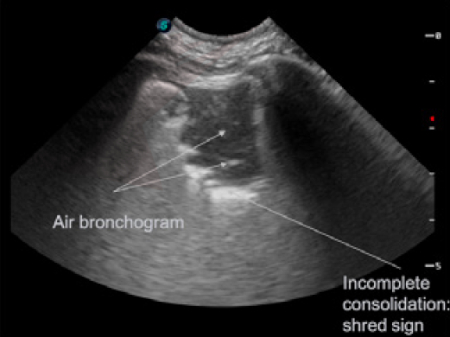
State Of The Art Lecture Advanced Lung Ultrasound Subpleural Consolidations And Bronchograms Wsava 2019 Congress Vin
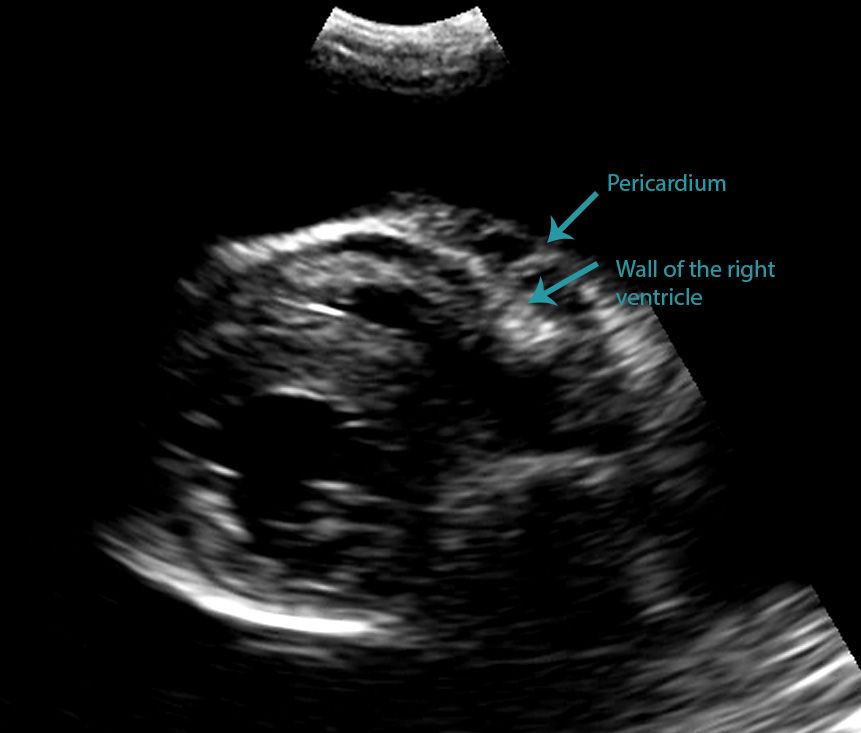
Differentiating Pericardial From Pleural Effusion Animal Ultrasound Association

How To Ultrasound Detection Of Pleural Fluid Case Study Video Youtube

10 Year Old Male Castrated Domestic Medium Haired Cat American College Of Veterinary Radiology

Cat Of Figure 1 Thoracic Ultrasound Revealed A Mild Hypoechoic Download Scientific Diagram
Front Line Ultrasound Imaging Of The Feline Urinary
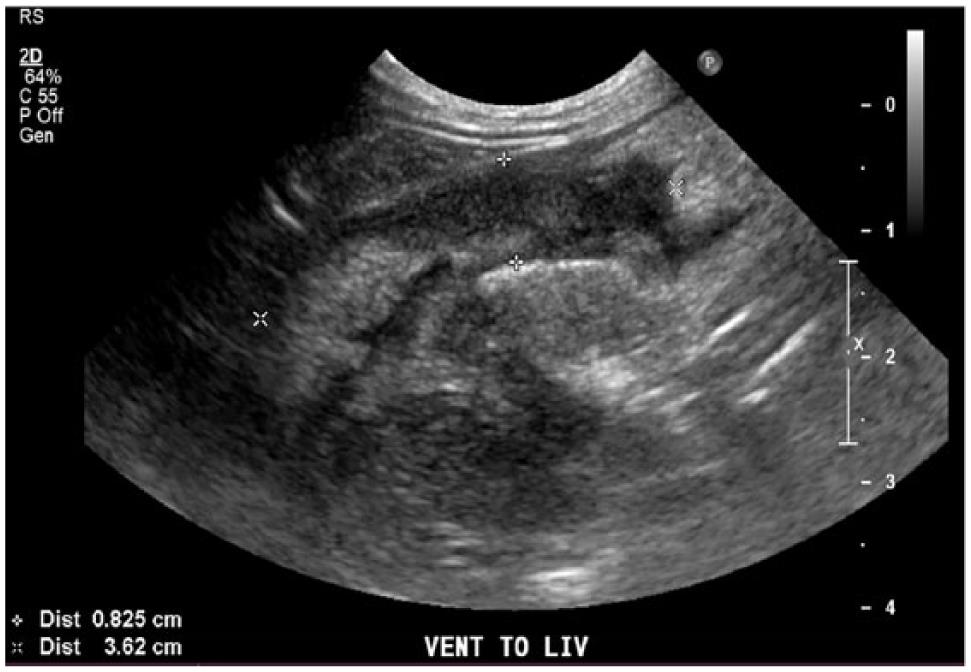
Spontaneous Cholecystopleural Fistula Leading To Biliothorax And Sepsis In A Cat

Midscapular Thoracentesis Ultrasound Training Model Ultrasound Training Ultrasound Emergency Medicine

Midscapular Thoracentesis Ultrasound Training Model Ultrasound Training Ultrasound Emergency Medicine

Differentiating Pericardial From Pleural Effusion Animal Ultrasound Association

Different Types Of Pleural Effusion On Ultrasound Scan A Exudate B Download Scientific Diagram

2018 Now Available For Free Download In Vetbooks Ir Vetbooks Free Veterinary Vet Veterinarian Vets Dvm Veterinary Radiology Radiology Online Textbook

Top 5 Ultrasound Scenarios In General Practice Clinician S Brief